
This article talks about the spectrum analyzer online and how to use it to improve your mix and achieve more balanced mixes. You probably have seen somewhere that you should trust your ears when mixing, and while part of that is, of course, true. But why wouldn’t you use the tools to help you see what’s happening sonically in your song?
It’s like being a pilot and turning all the instruments off because you should trust your eyes. Well, that doesn’t make sense, does it? As audio engineers, we utilize the spectrum analyzer to visually observe the frequencies of a sound, enabling us to understand its graphical representation.
So, if we use it correctly during the mixing process, it’ll help us to get the tonal balance in place. Let’s jump right into how to use spectrum analyzers to improve mixing.

Let’s Briefly Understand Spectrum Analyzer Online
A spectrum analyzer is a measurement device that shows the frequency analysis of incoming audio signals in real-time. They display results with the help of a graph. Pitch and frequency expressed in Hertz are displayed on the horizontal axis. The vertical axis uses decibels as a unit to display the amplitude of frequencies.
Understanding Frequency Spectrum
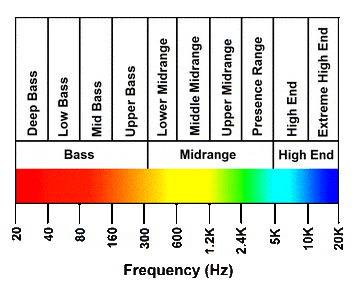
The frequency spectrum shows the span of audible frequencies. Normal audible frequency for humans is between 20 Hz to 20,000 kHz.
The frequency spectrum is split into seven bands on many charts.These bands describe each frequency range’s tonal characteristics. The seven bands of frequency are as follows:
- Sub-bass (20 Hz – 60 Hz)
- Bass (60 Hz – 250 Hz)
- Low Midrange (250 Hz – 500 Hz)
- Midrange (500 Hz – 2 kHz)
- Upper Midrange (2 kHz – 4 kHz)
- Presence (4 kHz – 6 kHz)
- Brilliance (6 kHz – 20 kHz)
Let’s Learn How to Use Spectrum Analyzers to Improve Mix
A spectrum analyzer can be used in various ways. Discover five ways to use a spectrum analyzer to enhance your mix or listening environment:
Determine Resonance Issues
Resonance involves the concentration of energy at specific frequencies in a sound, contributing positively or causing unpleasant disruptions. Harsh resonance spikes, detected easily through a spectrum analyzer, manifest as sharp peaks or broader bumps in midrange or low frequencies. Identifying problematic resonances is vital for a balanced mix.
Use a spectrum analyzer plugin at the end of the device chain to spot frequency spikes and address them with EQ, filters, or compressors. This corrective approach ensures a more pleasing audio output.
Furthermore, analyzing resonance peaks assists in determining a signal’s fundamental frequency, aiding in refining overall sound quality. Effectively managing resonances is crucial for achieving optimal audio production results.
Determine Undesired Low Frequencies and Irregularities
Identifying problematic low frequencies can be challenging in poor listening environments or with inadequate monitors that fail to reproduce the lower spectrum accurately. Determining the optimal cutoff frequency for high-pass filtering presents a delicate balance. Setting it too low may leave disruptive frequencies while cutting too much can strip away a sound’s fullness and body.
To address this, a spectrum analyzer proves invaluable. Insert a spectrum analyzer plugin at the end of the device chain and play a section featuring the track’s lowest notes or chords. Examine the analyzer’s display for the lowest frequency bump, representing the sound’s fundamental frequency.
Safely cutting anything below this point addresses excess low frequencies without compromising the sound’s body and timbre. This technique is also effective for identifying and addressing excessive high frequencies, offering a comprehensive approach to frequency management in audio production.
Contrast Two Frequency Results
Ensuring a harmonious mix involves preventing conflicts between different elements. Each sound should carve out its own space, both in the frequency spectrum and stereo field. When two or more sounds occupy a similar frequency range, they can clash, leading to a phenomenon known as frequency masking. This interference hampers the clear perception of individual sounds and introduces various mix issues.
While some conflicts are audible, visual aids can be beneficial. Many spectrum analyzer plugins offer a feature allowing the simultaneous display of multiple frequency responses. This functionality aids in comparing sounds and pinpointing conflicting frequency areas.
For this method, use a spectrum analyzer plugin with an external sidechain input. Place the plugin at the end of the device chain and route the signal from the track to be compared into the plugin using the sidechain input. Once problematic areas are identified, employ an EQ to separate and clarify the sounds, ensuring each element occupies its distinct sonic space in the mix.
Analyze the Tonal Balance of a Mix
Tonal balance refers to the even distribution of energy across the frequency spectrum, influencing the perceived timbre of a mix or sound. Achieving a balanced mix is essential for creating a pleasant auditory experience that translates well across various speaker systems. In a tonally balanced mix, there is a consistent frequency response and equal perceived loudness across the spectrum, ensuring a smooth blend of lower and higher frequencies.
Spectrum analyzers serve as primary tools to monitor tonal balance. By inserting a spectrum analyzer plugin at the end of the master channel’s device chain and setting the response to a slow speed, short-term peaks are averaged, revealing a smoother frequency curve. Analyzing the results helps identify significant peaks or valleys, which can then be addressed using EQ adjustments in the mix.
Spectrum analyzers are also valuable during mastering, allowing for a comparison between your mix and a commercial reference track. Routing the reference song into the analyzer helps ensure that your mix aligns with industry standards, bringing it to a commercial level of quality.
Check the Acoustics of the Rooms
Utilizing spectrum analysis aids in understanding your listening environment’s frequency response. Various acoustic measuring tools can assess a room’s unique frequency curve, revealing areas with bumps or gaps.
Recognizing your room’s characteristics is crucial for compensating during mixing and understanding the impact of acoustics on your mixes. If your listening environment has deficiencies, considering acoustic treatment may be beneficial for improving the overall quality of your audio production.
Takeaways
While spectrum analyzers provide valuable visual insights for better mixing decisions, it’s essential to trust your ears. View visual feedback as a supportive tool to validate auditory perceptions. With experience, your ears will intuitively guide adjustments. Spectrum analyzers serve as aids in the learning process, complementing your evolving ability to discern and address audio nuances.
Click here to download our free software and support our cause of helping students and engineers and making our contribution to the advancement of science and technology.

