
Are you fed up with being unable to identify the cause of signal distortion or interference as an engineer? Are you sick and weary of trying to figure out where signal distortion or interference is coming from as an engineer? These issues can seriously damage your equipment and result in expensive downtime, whether they are in a power line or a radio transmission. The challenge is that a lot of troubleshooting techniques take a long time and don’t work. However, there is a fix! You may rapidly locate the issue’s source and get your equipment operating again by learning how to operate and read a spectrum analyzer online.
So, if you’re ready to master this art, continue reading. This article explores how to use a spectrum analyzer to identify and address any issues with distortion or interference. Let’s dive in!
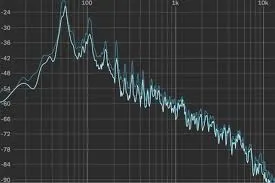
Spectrum Analyzer’s Display Components
In order to read a spectrum analyzer accurately, one must fully comprehend each of the individual components of the display. Every component offers crucial information for diagnosing and resolving signal problems.
A spectrum analyzer’s primary display components are the scale, center frequency, span, vertical and horizontal axes, and scale. An overview of the display components are as follows:
| Display Element | What They Represent |
| Horizontal axis | The frequency band is displayed on the analyzer’s horizontal axis using a logarithmic scale that runs from low to high. |
| Vertical axis | The vertical axis shows amplitude or signal strength. |
| Scale | The range of frequencies and amplitudes displayed on the readout of the display is determined by the scale. Typically, it is made up of lines that, at regular intervals, represent various voltage levels. |
| Center frequency | As the name suggests, the center frequency is the frequency at the middle of the screen. |
| Span | The span, which can change based on how much you want to observe, is the range of frequencies that the spectrum analyzer displays. |
You can detect and resolve signal problems more rapidly if you are aware of every component of the display. Let’s examine each component and their interrelationship in more detail.
Spectrum Analyzer Online Functions
A measurement instrument called a Spectrum Analyzer Online is used to view and examine a signal’s spectral content. In order to do this, it measures the input signal’s magnitude in relation to its frequency across the whole frequency range.
Consider this as a way to view the “frequency fingerprint” of a transmission. You can use this fingerprint to ascertain the signal strength of electronic equipment and the composition of various frequency components in that signal.
Its primary test features identify
- Power
- Frequency
- Amplitude
- Bandwidth
- Phase and other parameters of a signal
A Spectrum Analyzer Online can be used for a wide range of tasks. A spectrum analyzer can be used for audio signal engineering, radio, and wireless communication. They will also support the optimization and troubleshooting of electronic wireless networking hardware.

Making Modifications
Knowing how various features and settings impact the data shown is essential when using a spectrum analyzer. You can maximize the instrument’s functionality and produce more precise measurements by adjusting different settings.
Three crucial configurations to be aware of are
Gain:The gain establishes the amount of applied amplification to the signal and regulates the sensitivity of the instrument. Raising the gain can improve the display’s visibility of weak signals. On the other hand, saturation or distortion of the signal might result from setting the gain too high. To obtain a precise and unambiguous signal readout, it is essential to adjust the gain appropriately.
Scan rate: The instrument’s scan rate determines how quickly it scans the frequency spectrum. A faster display update can be achieved with a greater scan rate, but the resolution and measurement accuracy may suffer as a result. Higher resolution and precision can be obtained at a lower scan rate, but the display will refresh more slowly. It is important to choose the right scan rate based on the specific signal measurement.
Attenuation: The signal’s amplitude is decreased by attenuation before being amplified by gain. Saturation and distortion of the signal can be avoided by lowering its amplitude. Setting the attenuation correctly is crucial, especially when working with high-power signals, in order to obtain a clear and accurate signal readout.
How to Interpret the Findings
At first, reading a spectrum analyzer’s results can be intimidating. However, if you have a firm grasp on the functionality of the instrument and its display aspects, it becomes rather simple. Here’s how to accurately read a spectrum analyzer step-by-step.
Step 1: Become Acquainted with the Display Components
It’s vital that you become familiar with the various components of the display before taking any measurements. These consist of the span, center frequency, amplitude axis, frequency axis, and any potential markers or traces. Ensure that you know what each component stands for.
Step 2: Connect the Signal
Plug the signal to be measured to the input of the spectrum analyzer. Make sure that the signal and its level are both within the fluctuating range of the instrument and the instrument’s frequency range.
Step 3: Modify the Configurations
To maximize the display for your measurement, make necessary adjustments to the gain, attenuation, and scan rate after connecting the signal. For a precise and clear signal readout, set the gain appropriately.
Step 4: Examine the Display
Take note of the frequency and amplitude of the signal by looking at the display. Search for any undesirable frequency components as well as any peaks or troughs. Measure the signal’s precise frequency and amplitude using the markers or trace function.
Step 5: Evaluate the Outcomes
Assess the measurement outcomes by contrasting them with the anticipated outcomes or signal parameters. Find any problems or differences from the anticipated outcomes and adjust the troubleshooting accordingly.
Now that you know how to read the data here are some potential displays to help demonstrate the above-described stages.
| Scenario | Explanation |
| A single-frequency signal | A single-frequency signal with a distinct peak at the anticipated frequency is visible on the display. The signal’s amplitude falls within the expected range. The frequency of choice is set as the central frequency. Everything appears to be as it should be. |
| Interference signal | Multiple frequency peaks on the display suggest that interference is present. The signal’s proximity to other signals is the cause of this. You must change the gain since the interference signals’ amplitude is greater than the desired signal. By adjusting the gain, the measurement’s precision will increase and the interference signals’ amplitude will decrease. |
| Distorted signal | Signal distortion is indicated by the display, which shows a signal with a twisted shape. Incorrect attenuation or a high gain setting may be the cause of this, concealing lower-level signals. The signal has a smaller amplitude than anticipated. Take action to lessen distortion by raising the attenuation or lowering the gain. |
These are some illustrations of how to interpret various spectrum analyzer display findings. You will be able to rapidly and precisely analyze the outcomes of your measurements with practice and experience. Now that you know the fundamentals of using a spectrum analyzer, go out and begin taking measurements!
Final Thoughts
And that’s a wrap. We’ve tried to cover every minor detail about reading spectrum analyzer online like a pro! From signal connection, optimum setting adjustments, and observing the display, we’ve discussed it all.
With practice and expertise, you will be able to rapidly and precisely analyze the results of your measurements, even if it may seem scary at first.
